Strep Throat: What you need to know

What is Strep Throat:
Viruses are the most common cause for a sore throat. Strep throat is an infection in the throat and tonsils caused by a bacteria known as group A Streptococcus.
The signs and symptoms of Strep throat differ from a virus.
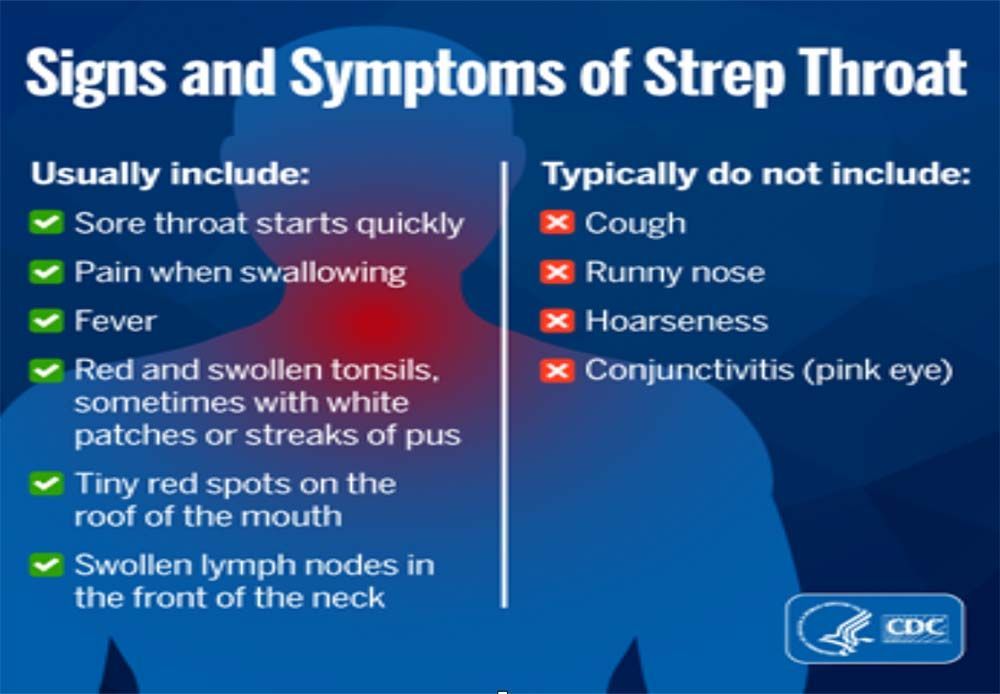
Other symptoms may also include a headache, stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting especially in children. Sometimes a patient with strep throat may develop a rash known as scarlet fever.
How do you get strep throat:
Group A strep lives in the nose and throat and easily spread to other people by talking, sneezing, or coughing through small respiratory droplets that contain the bacteria. To those exposed to Group A strep, it takes usually two to five days for someone to become ill with strep throat. Close contact with another person with strep throat is the most common risk factor.
Though anyone can get strep throat, it is more common among children ages 5 to 15 years old than in adults. It is very rare in children younger than 3 years old. Adults who are at increased risk for strep throat include parents of school aged children and adults who are in frequent contact with children such as teachers and daycare workers.
Testing and Treatment:
After examining the patient with a sore throat, if indicated, the provider will swab the throat to test for strep throat. There are two types of tests: a rapid test which will be performed at the time of the visit and quickly determine if there is group A strep. If the test is positive, the patient will be prescribed antibiotics. Amoxicillin is the recommended first drug of choice while other antibiotics are prescribed for those patients who are allergic to penicillin.
Antibiotics help prevent the spread of the infection
- Patients with strep throat should stay home from school, work, or daycare until they have been taking antibiotics for at least 12 hours and no longer have a fever
- Complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed and do not stop even if you start to feel better
For children and teens, a throat culture should also be obtained and sent to the lab for testing. While this test takes more time than the rapid test, it is important in this age group to perform the test to identify untreated strep which could cause rheumatic fever if left untreated. According to the CDC, it is usually not necessary to do a throat culture for an adult with a negative rapid strep test since they are generally not at risk for rheumatic fever. Patients without symptoms who test positive usually do not need antibiotics.
How to protect yourself and others from getting strep is to:
- Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze by using a tissue or your sleeve not your hand
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer when soap and water is not available
- Avoid using glasses, utensils, plates after someone who is sick uses them.