A cough plays a significant role in fighting off cold and flu viruses that infect the body through the nasal lining. It usually starts as a tickle in the throat that turns into a full-blown dry cough indicating a serious infection of the upper respiratory tract. Coughing is a body’s defense mechanism that facilitates the expulsion of foreign particles, microbes, and excess mucus from the respiratory tract, which prevents infections, and inflammation of the lung.
It occurs when the nerves in the larynx become irritated by cold air, allergies, infections, or dust particles. A cough can either be a conscious act that is voluntary or uncontrollable and involuntary. This article discusses whether coughing is a symptom of cold and what to do about it.
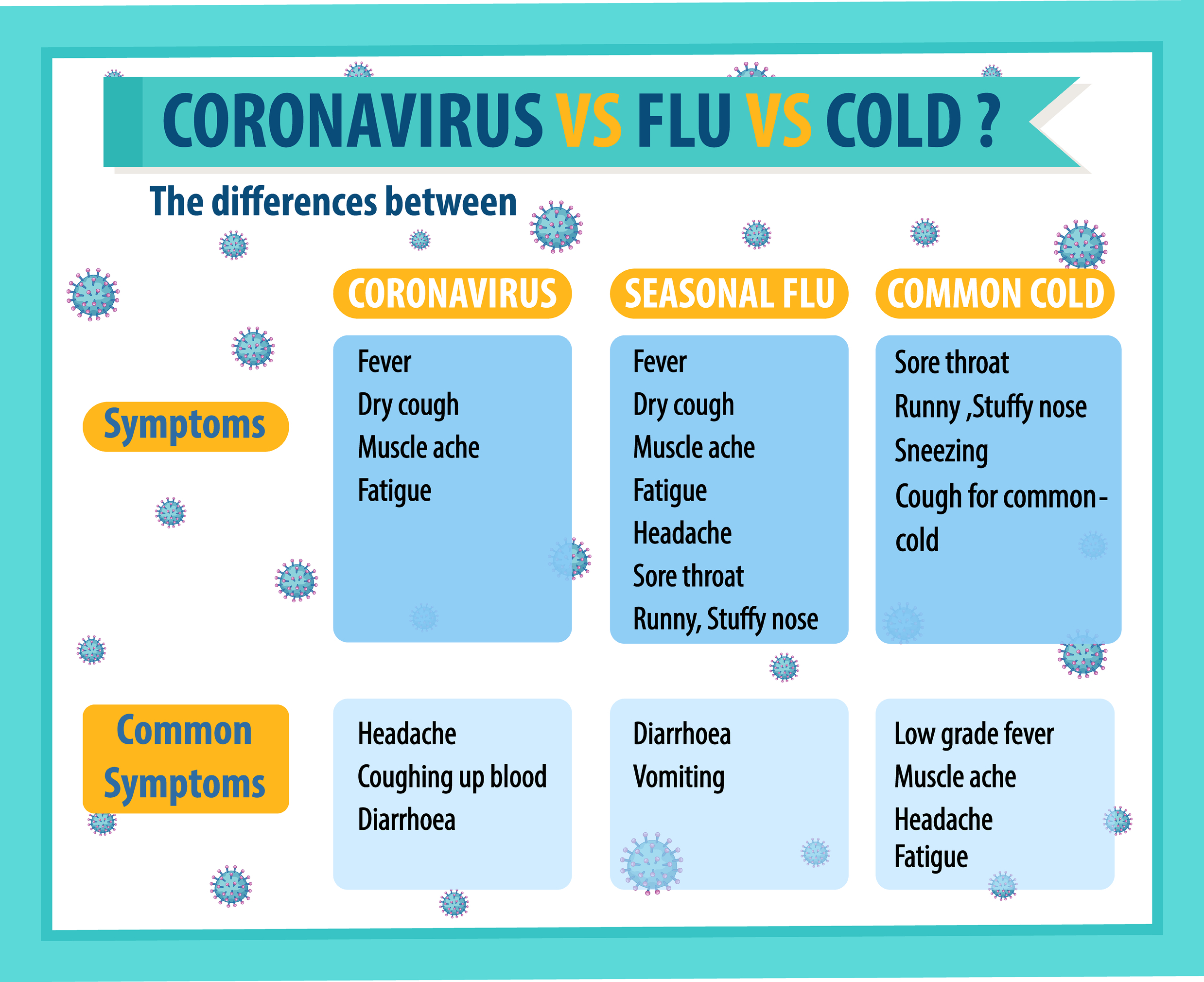
How is Cough Related to Cold?
A cold usually starts with a sore throat and you may start coughing as a way to clear the mucus or foreign particles blocking your throat. You may start experiencing other symptoms such as a runny nose, sneezing, and fatigue. During the first few days, you may experience a mild cough that can worsens over time. A cough that produces dark or thick mucus is an indication that you have a bacterial infection. These symptoms may start between 1 to 3 days after being infected with a cold virus and can last up to a week.
A cough is usually considered an early symptom of cold because your body’s immunity system tries to expel the microbes and other foreign particles that block your respiratory airways. The damage caused to the nasal cell lining can lead to severe coughing and may require antibiotics for quick relief.
Is it a Cold or an Allergy?
Diagnosing and providing treatment for a cough is sometimes difficult because many patients are uncertain about the exact cause of their condition. As a result, most people fail to seek proper medical attention and instead, take incorrect medications that can be detrimental to their overall health.
A dry cough can either be a symptom of a cold or an allergic reaction. It is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as nasal congestion or runny nose that occur simultaneously for an individual suffering from an allergic reaction or a common cold. An allergic cough occurs when an overactive immune system responds aggressively to foreign substances in your body. This triggers the defense system, which fails to distinguish substances that are harmful from those that are harmless. There are situations when you may experience persistent cough for several weeks after catching a cold.
Any small amount of dust or cold air can trigger a cough when your respiratory airways are overly sensitive. It can also be caused by pertussis infection that occurs in both adults and children. If your cough does not seem to go away on its own then you might consider using antibiotics recommended by your doctor. However, antibiotics may not be effective if your cough becomes chronic. It is always important to seek medical help if your cough does not improve even after a cold.
Cold Symptoms and Causes
Different types of viruses often cause a cold. One of the common viruses that cause cold is rhinovirus. Once you get infected, your body reacts by producing antibodies that fight the foreign virus. As a result, it causes an increase in mucus production, which can lead to a runny nose. It also brings about nasal congestion that makes it hard to breathe. When this happens, your body responds through sneezing and coughing.
Sneezing occurs because of irritation in the nose while coughing is caused by the increased amount of mucus dripping down your throat. You can catch a cold through the air or in direct contact with an infected person. Other symptoms of cold include fever, tickly throat, chills, headaches, mild fatigue, watery eyes, and fussiness. The duration of the symptoms may vary depending on an individual but usually manifest within one to three days after exposure to the virus.
A cough is one of the symptoms of cold caused by the reaction of your body’s defense system to the cold-causing virus. However, a persistent cough that continues a few weeks after your cold symptoms are gone could be a sign of an underlying health problem. Children are more likely to suffer from a cold than adults because of their immature immune systems. It is important to seek medical attention if your condition does not seem to improve on its own or with self-treatment at home.
